Overview videos
Power booster
The Power Booster system can be used with our standard vacuum dispensing system to achieve a suction height of up to 25m.
U-system
Patented system for sampling in conjunction with a modified vacuum dosing system, suitable for suction heights of up to 30 metres. Compressed air is required for this system.
40 m pressure conveying system
With the pressure conveying system, a sample can be conveyed up to 40 metres using a special pressure-vacuum probe. Compressed air is required for this system.
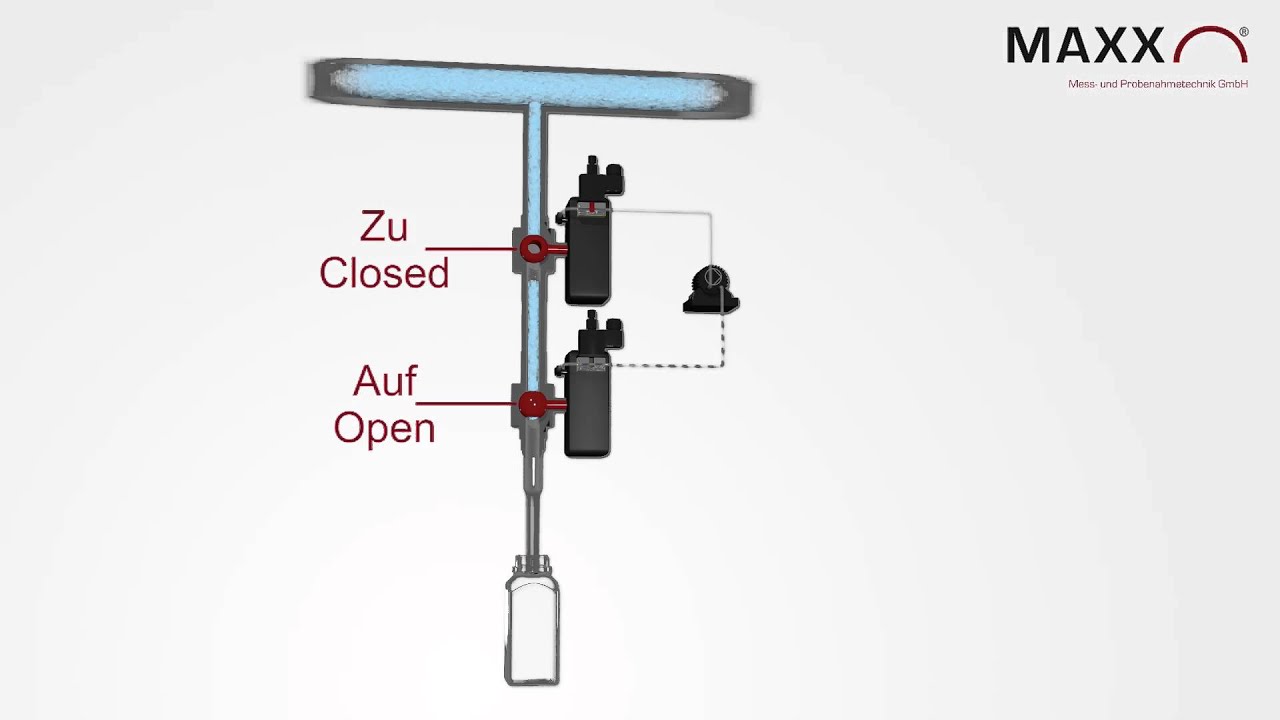
DK double ball valve
The DK system is especially suitable for sampling from pressurised lines with up to 25 bar. With an optional air connection on the volumetric tube, it is also possible to blow out if the pressure of the compressed air is higher than the line pressure in order to minimise the dead volume. This dosing system can also be used in Ex zones, as the ball valves are only operated with compressed air. Compressed air is required for this system.
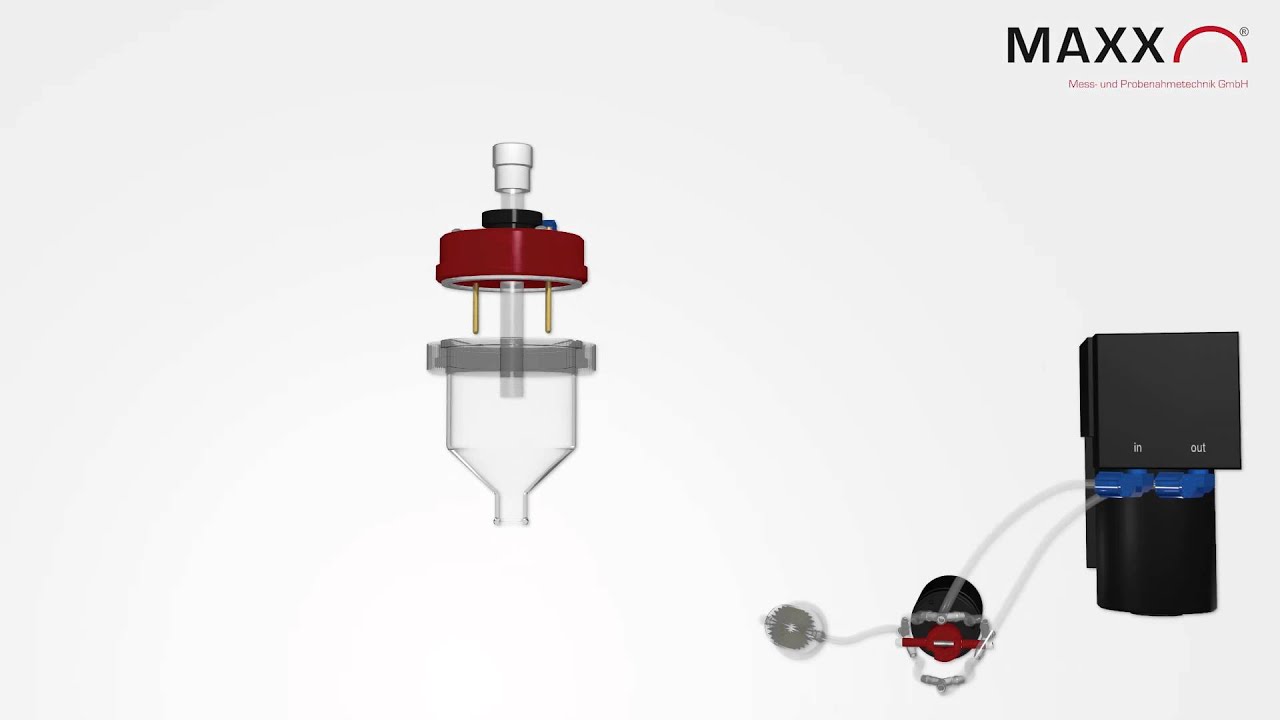
Vacuum system
This is the most common sampling dosing system in Europe and has been used thousands of times. A diaphragm compressor is used to generate pressure (free blowing) and vacuum in the dosing vessel in order to aspirate the sample. The system is characterised by a very high dosing accuracy and has a comparatively low energy requirement, with virtually maintenance-free and therefore cost-effective (24/7) continuous operation.
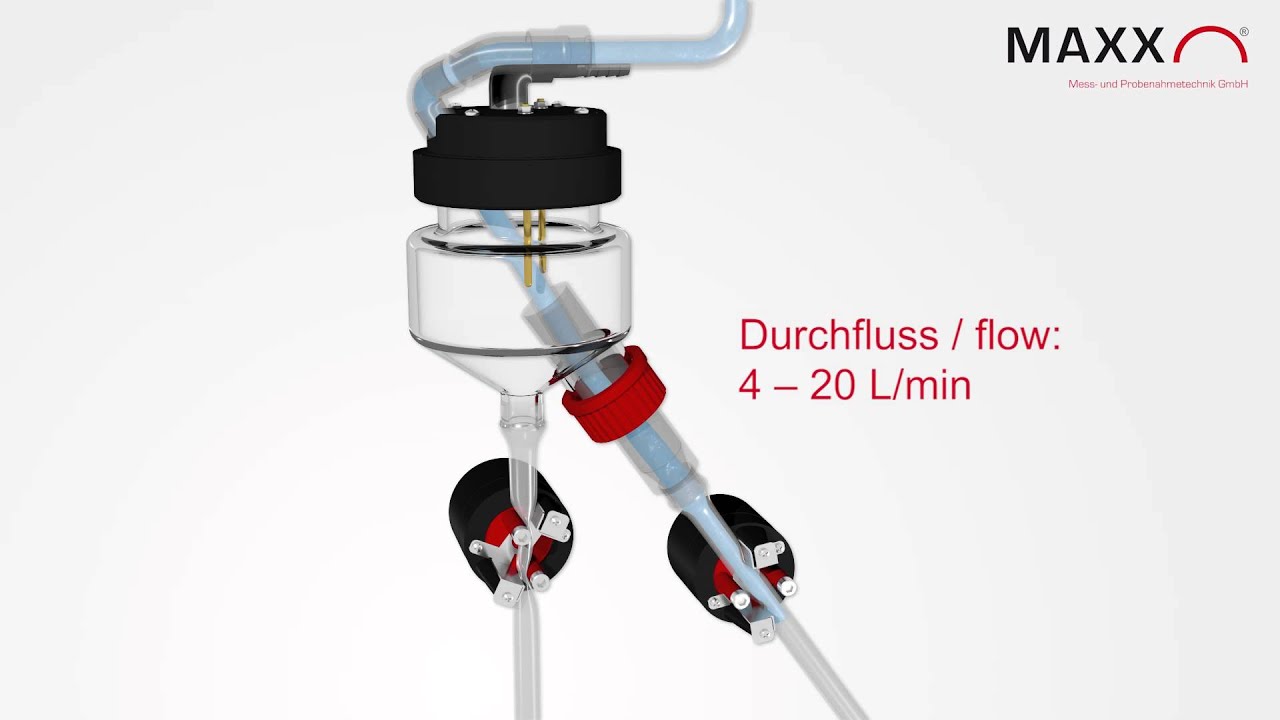
Flow-through-system
The flow-through system is suitable if samples are to be taken with a continuous flow through the sampling device. An unpressurised outflow must be possible on site. The advantages are: can be used with variable inflow, also suitable for pressurised lines (with on-site volume limitation to 3-20 l/min), very high dosing accuracy, virtually maintenance-free.
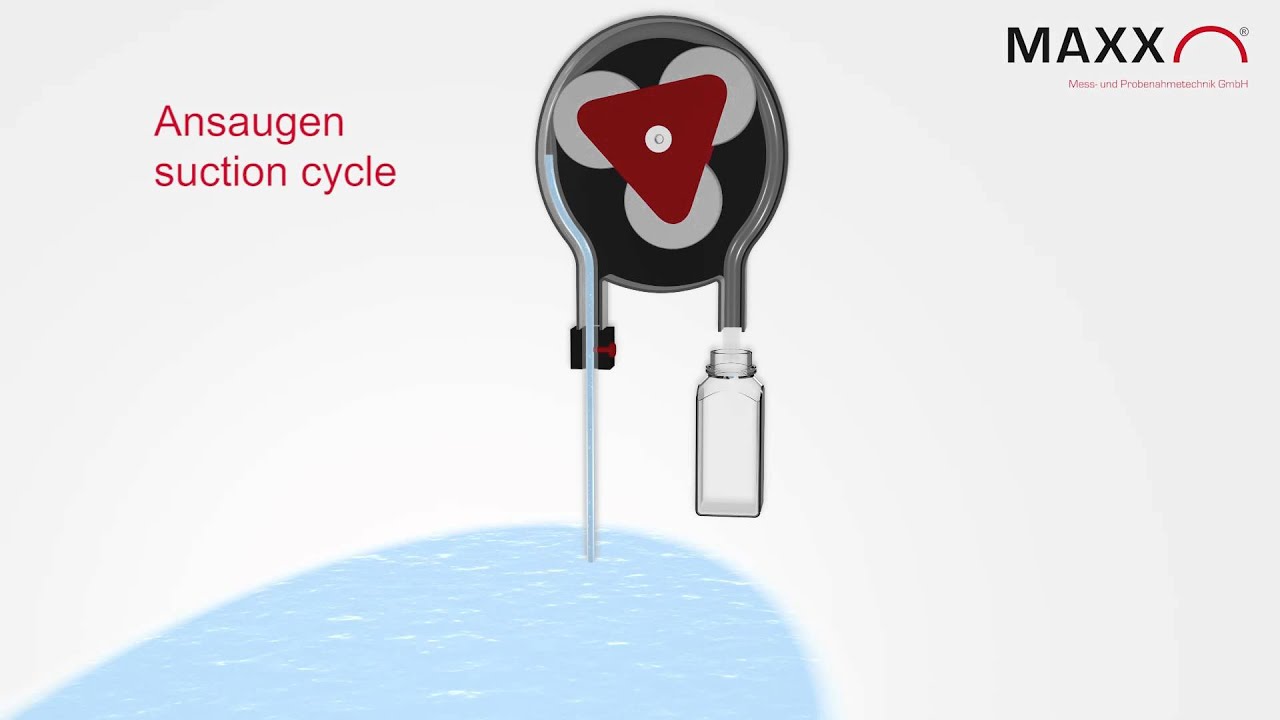
Peristaltic pump
Probably the most widely used sampling system in the world. It is technically the simplest system for automatic sampling. The peristaltic pump generates both pressure for blowing out and vacuum for sucking in the sample without any other components, such as valves etc. The disadvantages are:
- Significantly higher energy consumption compared to the vacuum system and therefore less operating time with battery-operated (portable) devices.
- Increased wear of the pump hose if solids (sand, stones) are sucked in.
- Higher operating costs (hose replacement)
- Dosing quantity and accuracy are influenced by hose ageing and temperature changes.